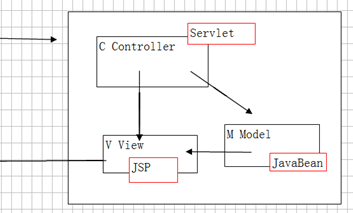
MVC
MVC基本定义
一种软件设计模式,B/S架构都支持。例如:java、.net、php等
思想:业务逻辑处理与数据显示相分离。
Model:模型,用于封装数据
View:视图,用于显示数据
Controller:控制器,用于控制正常执行。
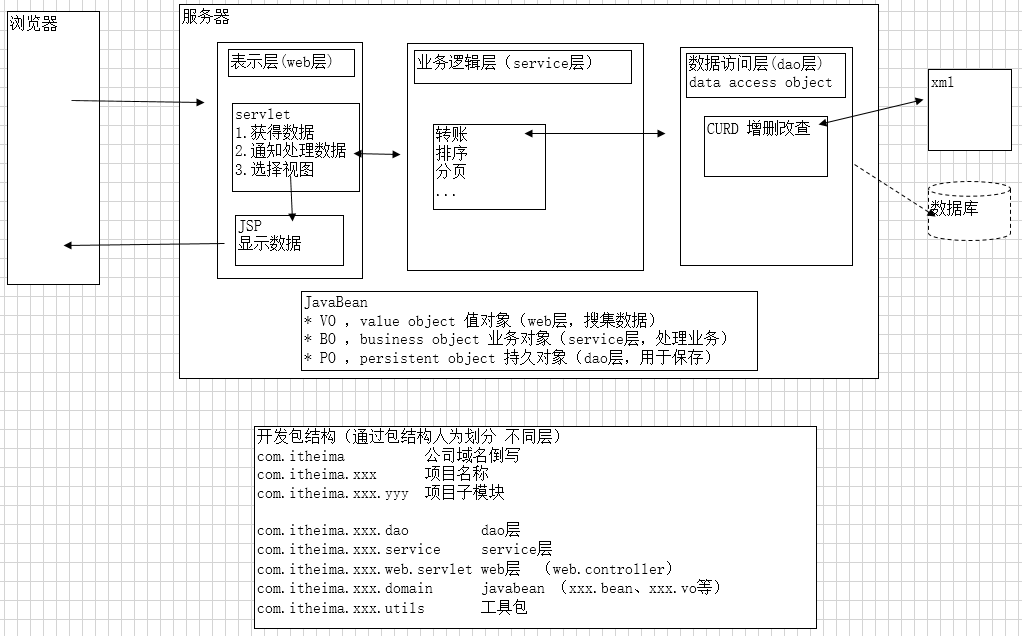
Web项目分包结构
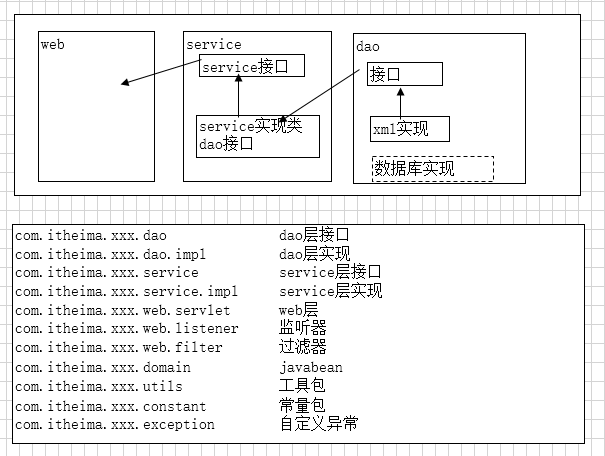
面向接口编程
用户管理系统
功能分析
- 注册
- 登录
- 查询所有用户
- 查询详情
- 修改用户
- 删除用户
技术分析
- MVC三层架构
- xml/dom4j
- servlet/jsp/javabean
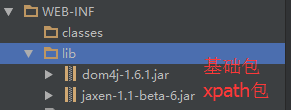
导入需要的jar包
解析xml需要
包结构
com.lujiahao.web.servlet web层
com.lujiahao.service service层
com.lujiahao.dao dao层
com.lujiahao.domain javabean
com.lujiahao.utils 工具包
数据库
暂定使用xml
xml内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<users>
<user id="u001">
<username>jack</username>
<password>1234</password>
<gender>男</gender>
<age>18</age>
</user>
</users>
JavaBean
数据库定义完成之后就开始编写JavaBean
dao层实现
随便写点数据的增删改查功能
数据校验
一般都是写在和servlet同级的包里面
这种类型的bean里面所有的字段都是字符串
用于获得浏览器发送的数据,并对数据的有效性进行校验
- 提供校验validate()
- 记录每一项的校验结果
具体代码实现:
public class UserFormBean {
private String id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String repassword;
private String gender;
private String age;// 因为服务器传过来的数据都是string类型的
public UserFormBean() {}
public UserFormBean(String id, String username, String password, String repassword, String gender, String age) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.repassword = repassword;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getRepassword() {
return repassword;
}
public void setRepassword(String repassword) {
this.repassword = repassword;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
// 记录错误信息 key:对应字段 value:提示信息
private Map<String,String> errorMsg = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 校验方法
*/
public boolean validate() {
boolean temp = true;
// 用户名不能为空
if (username == null || "".equals(username)) {
errorMsg.put("usernameMsg","用户名不能为空");
temp = false;
}
if (password == null || "".equals(password)) {
errorMsg.put("passwordMsg","密码不能为空");
temp = false;
} else if (! password.equals(repassword)){
errorMsg.put("repasswordMsg","确认密码和密码不一致");
temp = false;
}
return temp;
}
public Map<String, String> getErrorMsg() {
return errorMsg;
}
}
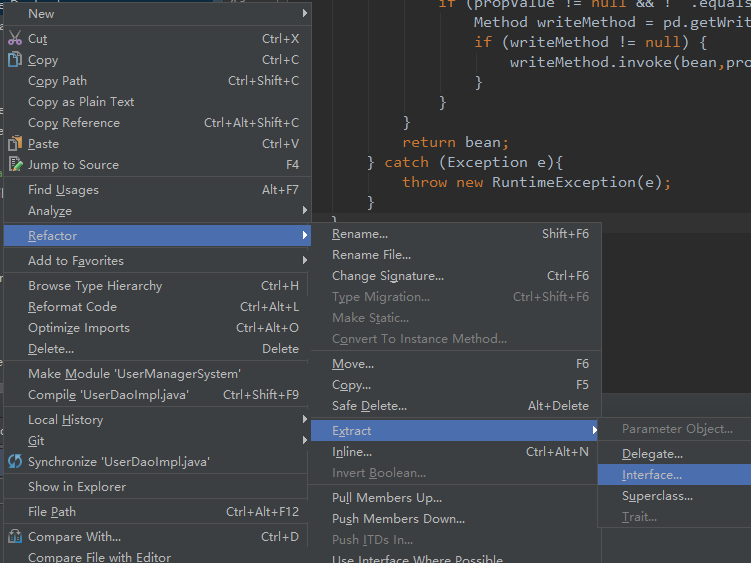
使用接口
三层结构每一层都应该是有接口和具体的实现类
使用Intellj重构代码
BeanUtils
通过封装的类来简化参数的自动封装
使用了反射和内省
初始代码:
// 1.获取请求参数
String id = request.getParameter("id");
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
String repassword = request.getParameter("repassword");
String gender = request.getParameter("gender");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
/**
* 数据校验
*/
UserFormBean userFormBean = new UserFormBean(id,username,password,repassword,gender,age);
封装后的代码:
UserFormBean userFormBean = MyBeanUtils.populate(UserFormBean.class,request.getParameterMap());
BeanUtils详细代码:
public class MyBeanUtils {
/**
* 创建JavaBean实例,并自动将对应的参数进行封装
* @param beanClass
* @param parameterMap
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public static <T> T populate(Class<T> beanClass, Map<String,String[]> parameterMap){
try {
// 1.使用反射创建javabean实例
T bean = beanClass.newInstance();
// 2.获得javabean属性(property username-->setUsername()-->执行set方法,数据来自map
// 2.1获得所有属性--使用内省(java.beans.Introspector):jdk提供工具类,用于操作javabean
// BeanInfo jdk提供用于对javabean进行描述(封装)对象
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(beanClass, Object.class);
// 2.2 获得所有的属性描述对象
PropertyDescriptor[] allPd = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : allPd) {
// 2.3 获得属性名称
String propName = pd.getName();
// 2.4 获得表单中对应的数据
String[] allValue = parameterMap.get(propName);
if (allValue == null) {
continue;// 当没有值的时候就跳过这个字段
}
String propValue = allValue[0];
// 2.5 如果有值,将执行set方法
if (propValue != null && !"".equals(propValue)) {
Method writeMethod = pd.getWriteMethod();// 相当于set方法 getReadMethod--相当于get方法
if (writeMethod != null) {
writeMethod.invoke(bean,propValue);
}
}
}
return bean;
} catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}






